So you’ve decided that you want to quit your day job and start your very own ecommerce empire. That’s great!
But before you become the next Jeff Bezos (and definitely before you quit your job!), it’s worth spending some time thinking about a business plan. In this article, we’ll dive into the key elements of an ecommerce business plan, which is very different than writing traditional business plans.

Why You Should Create a Business Plan
We know that starting an ecommerce business is exciting, and it can be tempting to jump right in without constructing a business plan. READ: PLEASE DON’T DO THIS.
If you haven’t put your ideas, questions and concerns on paper, then you haven’t given your business model enough thought.
Taking the time to write a business plan might seem like a lot of work, but it can save you a lot of time and money in the long run by better preparing you for potential challenges and opportunities that you’ll face as a first-time entrepreneur. Think of it as a roadmap for your new business venture.
It’s exciting to start your own ecommerce business. However, you want to be well prepared and not jump into anything without having a solid, foolproof ecommerce business plan in place.
After all, you wouldn’t jump out of a plane without a parachute, so why start a business without a safety device in place? That safety device is your business plan.

The business plan is the brainstorming process that ensures your concept and goals are realistic.
This is more than just mental notes. True business plans take your ideas, questions, and concerns and put those in writing.
As you start creating your business plan, you’ll soon understand that it’s more than a single piece of paper with handwritten details on it. It’s a clearly constructed format of how your business will be created, how it will operate, and what you hope the future holds in terms of a successful ecommerce business.
When you write your business plan, be sure to have a target audience in mind. Are you going to look for investors or put a Kickstarter campaign into motion and use this as your descriptive platform? If so, make sure that your business plan contains everything the audience would want to know about your business (and more!). Many traditional funding solutions require a business plan in order to give you capital. However, there are alternative solutions, such as Payability that specialize in ecommerce and don’t require credit checks, a business plan, or any complicated paperwork. They can also get you approved in as little as 24 hours.
When your business plan is completed, you should have achieved the following goals:
- Knowledge: A greater sense of knowledge of the business aspects.
- Resources: The resources you’re going to need to make your business successful, such as partners, money, employees, etc.
- Road Map: Have clear set goals to take you from the very beginning of your business and onward.
- Viability: In other words, is your business possible? Will you have enough profit margins to keep the doors open long-term?
Now that you know why you should create a business plan, it’s time to move on to how you can create your business plan and get started putting your ecommerce business into motion.
How to Start an Ecommerce Business Plan
At the very beginning of the planning stages, it’s a good idea to develop a framework for your business model. This business model will continue to evolve as you create each section of your ecommerce business plan, so don’t strive for a perfect completed plan on the first try. You will be making tweaks to the plan of certain steps along the way.
There are many ways to sell products online and different business models to pursue. Research and learn from successful ecommerce business examples in the market. The exact business model you follow will be one that makes the most sense with your resources, skills, and interests.
In order to create the best online business plan with your product in mind, you need to figure out the following things:
What are you selling?
The first step to creating an online business is to learn the absolute basics of what you can sell.
- Physical products: Clothing, shoes, home goods
- Digital products: Software as a Service products, ecourses, ebooks
- Services: Consulting services, home cleaning
Who are you selling to?
- Business-to-Business (B2B): You are selling to organizations, corporations, and non-profits rather than individual customers
- Business to Consumer (B2C): This means you are selling to individual consumers rather than businesses
- Marketplace: You are acting as a middleman by bringing businesses and (B2B or B2C) customers to one website.
How are you sourcing your product?
- Manufacture in-house: You make your product or service in-house
- Third-party manufacturer: You outsource the manufacturing of your product or service to a third-party manufacturer
- Dropship: You partner with a dropship manufacturer. Basically, this means that they make your product, package it and ship it directly to your customer while your company handles the entire customer relationship.
- Wholesale: You buy goods or services from other companies in bulk and re-sell those products on your online store
Additional References
- Entrepreneurship: Business & Marketing Plans
- Small Business and Entrepreneurship
- Entrepreneurship Resources
- Business Plan Resources
Executive Summary

The executive summary will be written according to your goals, and it’s recommended that this is done at the very end of your business plan completion. This will ensure that you include all of the important factors about your business and present your ideas in a concise and complete way.
Some of the features you’ll include in the executive summary include information showing that you’ve done your research, you have concrete sales forecasts, and the main details about your brand.
Business Model
When you’re figuring out your business model, you have to consider four different areas:
- Monetization strategy
- Product/industry
- Target market
- Sales channel
Monetization Strategy
The monetization strategy delves into the methods you are going to use to sell your products.
This strategy will look at different product monetization methods, including white label, private label, affiliate marketing, wholesale, dropshipping, and even selling ads.
Product/Industry
The product industry section is where you summarize your main niche.
For example, “Vegan Skincare Products.”
Target Market
In the target market section, you will write a sentence or so on who your target market, or ideal customer, is in the community.
If you’re selling vegan skincare products, your target customers might be women who embrace the vegan lifestyle and use natural skincare products in their daily beauty regimen.
Sales Channel
The sales channel refers to where you’re going to sell your products.
For example, you might be selling your products on your own website, and this should be entered in this section.
Business Overview

This next section covers your company overview.
This section of your business plan will cover various features of your company, including the following:
- Brand name
- Company type
- Domain name
- Value proposition
- Mission
- Vision
- Brand traits
Brand Name
The brand name section lists your business name or brand name.
This is an extremely important aspect of your business plan as it’s what will set the tone for everything that follows.
Pick a brand name that’s simple yet unique and is something that can be used in a wordplay manner, if desired, but not pun-worthy.
Company Type
The company is how your business operates. For example, you might label your business as an LLC, S-corporation, sole proprietor, or some other type of business organization.
The best way to determine how you should categorize your company is to speak to your accountant. There are various tax and legal aspects to forming your business in a certain way.
Speak with the professionals in the company and corporation formation field to determine how to label your company and which company type best benefits your business in a variety of ways.
Domain Name
This section is where you list your domain name.
Choose a domain name that is memorable and embraces the overall traits and features of your business.
And, when choosing a domain name, be sure to think of SEO aspects when doing so. You’ll find out just how much all of these things tie together and ensure a frequently-visited website is the end result.
Keep in mind that with ecommerce, the domain name is just as important as the brand name. Maybe even more so!
Value Proposition
A value proposition is a short, crisp statement that will gauge how clear your idea is. Write this section as if you had one minute to explain your business to a potential investor or customer and then practice it over and over again.
The value proposition can be used on your ecommerce store as your company description.
Here’s a good example: Say you’re looking to start a hiking company called Atlas Hiking Co. which sells premium performance hiking shirts. A possible company description could be the following:
Atlas Hiking Co. is a lifestyle hiking company that produces high-performance hiking shirts for outdoor lovers. Our proprietary SPF40 fabric is one of the lightest fabrics on the market, providing mountain lovers with maximum comfort, both from a breathability and sun-protection standpoint. Our product is made in the U.S.A. and a portion of our profits are donated to preserve national parks around the country.
Pay special attention to all the sensory words!
Mission
The mission statement in your business plan is the “why” of it all.
For example, why you started the business, why you are selling the products you are selling, etc., can all be added to this section of your business plan.
You can make this portion as simple or detailed as you like. Just make sure to properly and clearly explain your business mission.
Vision
The vision part of the business plan is your “how” in the grand scheme of things. It is the dream you have for your company and the path you’re going to take to realize that dream.
When you write the vision portion of the business plan, think long-term. What are you hoping to achieve, not just in the near future but for the long haul of the life of your business?
Look into the future and plan out where you see your business in 5, 10, even 20 years from now.
This will help you construct the rest of your business plan if you know where you want your business to head, now and in the future.
Brand Traits
The brand traits section is a short section in your company overview.
Basically, in the brand traits section you’re going to want to list three to five words that describe your brand.
Think of your brand personality and describe it using a few separate powerful words.
Personnel
The personnel section lists all individuals, including yourself, who will be involved in the daily operations of your business. You can create a separate section for a full operations plan or add that later.
Some business owners choose to handle all duties on their own or with a partner, while others will hire individuals to fill the following roles:
- CEO (usually the business owner)
- Management team
- Customer service/logistics
- Copywriter
- PR/Social media specialist
- SEO manager
- Advertising manager
Competitive Market Analysis

Here’s a fact you can bank on: there has never been a successful e-commerce entrepreneur that didn’t understand his/her target market cold.
That’s why this section is one of the most important in the entire business plan. It will force you to understand the industry in which you operate, the overall industry analysis and outlook, the existing competition, and your target customer demographic.
Market Segment
The market segment portion of the business plan will help you to put your ideas down on paper, make them more focused, and get your team together.
This area will include your niche selection, target market, and competitive analysis.
Niche Selection
The niche section provides an overview of your niche, why you selected it, whether there’s a micro niche included, and the type of niche you’ve chosen.
The purpose of this section is to crystalize the ideas that you have and make sure they are understandable and viable.
Target Market
The target market section covers an overview of your target market plus describes your market segments.
Ask yourself who your target customer is (population size, age, geography, education, ethnicity, income level) and consider whether consumers are comfortable with buying your product category online.
When listing the target market information, make sure to mention your target audience size as this is important for ensuring that your audience will be adequately covered.
Competitive Analysis
With the competitive analysis portion of your market analysis, you want to list your market leader and direct and indirect competitors.
After you mention who these entities are, you need to list the characteristics of each one, such as domain name, business model, monthly traffic, and pricing range.
However, before you even get started in writing this section, you need to spend several hours researching your target market.
Here are some of the most efficient ways to research a particular market:
Industry reports
Google is your best friend. Look for any recent industry reports on your market of choice. This will give you a good sense of how much growth the industry is experiencing, why this growth is happening, and what are the largest customer segments. In our example of Atlas Hiking Co., we should research the outdoor apparel market.
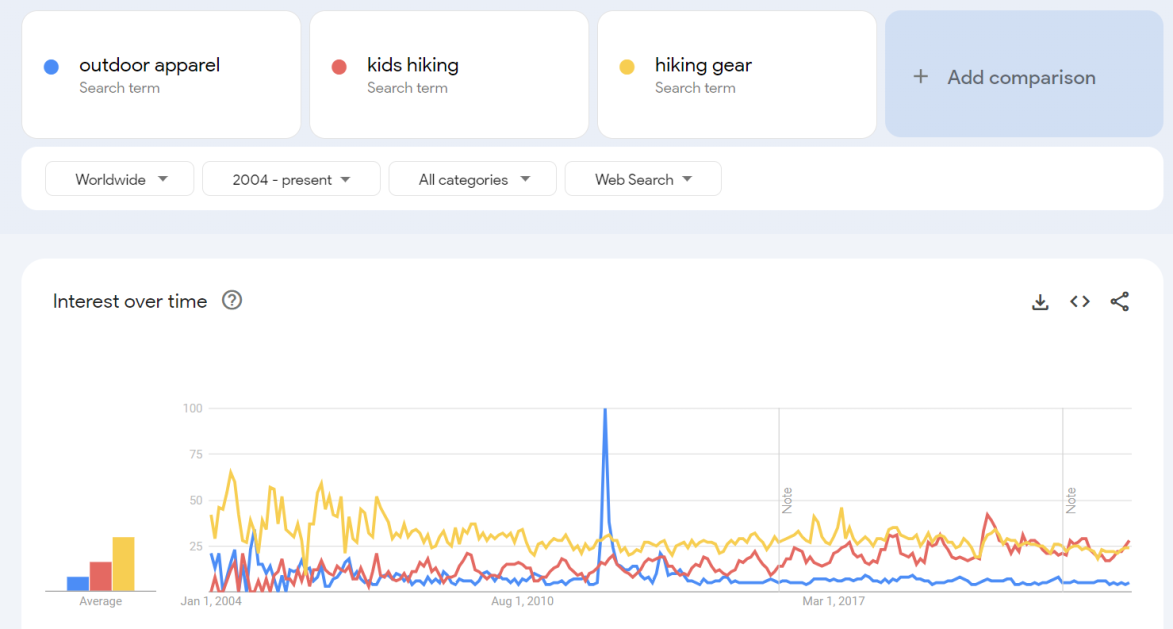
Let’s say that through our research of the outdoor apparel industry, we discovered that there was a huge boom in youth hiking apparel. Perhaps parents were increasingly concerned about their kids’ exposure to UV rays while hiking, so they began to spend more money on their kids. We could use this valuable information to guide our business strategy.
Shopping
There’s only so much you can read online. Go to a nearby store that sells similar products to yours and interview the store representative. The store rep has interacted with hundreds of interested customers, which can lead to thousands of valuable insights! It’s amazing how these insights can translate into a meaningful business opportunity.
Here’s an example:
If I were going into Billy’s Outdoor Store to research the outdoor apparel market, I would probably ask Billy the following:
- What are your best-selling products?
- What are your worst-selling products?
- Find products similar to yours and ask the representative his/her favorite features on products similar to yours.
- How much are customers generally willing to spend on these types of products?
- Do customers make repeat orders of any of these products?
- Do you get a lot of customers that are looking to buy last-minute hiking gear before they go on a hike?
Competition
Create an Excel spreadsheet of all of your competitors. In your spreadsheet, you should have the following columns:
- Competitor Name
- Website
- Price point
- Product Description
- Key Features (e.g., fabric, waterproof, slim fit, etc.)
What is the competition missing? Is there a gap in the offering? Where you can add some additional value?
After conducting the competitor analysis, Atlas Hiking Co. might find that the competition’s hiking shirts offer very few features at a low price point, but no one offers a luxury hiking shirt with additional features at a higher price point.
This is just an example of the types of insights one can gain from market research which can drastically alter your business model.
Keyword Research
By using Google’s keyword planner and trends pages, you can get a good sense of how in demand your product is and whether it’s trending upward or downward. Google is great for a general idea, just don’t bank on it.
Some other keyword tools you can use for keyword research include Ahrefs, JungleScout, and Viral Launch. Check out this list for more ideas.
Trade shows
Are there nearby trade shows that you can go to? Again, creating connections with other people in your industry is a surefire shortcut to countless hours of reading on the internet. Trade shows are also a great opportunity to talk to competitors, meet manufacturers, and better understand where things are heading in your industry.
Once you finish researching the relevant industry, you should summarize your findings by answering the following questions:
General Industry
- How big is the overall industry?
- How big is the specific sub-industry in which you intend to operate?
- Where has most of the historic growth in the market come from?
- Why is this the right time to enter this market?
- What are the sub-segments that are poised for future growth (e.g., youth apparel)?
Competition
- How crowded is the product category with competition?
- How is your competition distributing its product (online, retail, wholesale, etc.)?
- What’s missing from the competition’s product offering?
Products and Offers

So we know we want to sell hiking shirts, but how do you research specific products?
But for some of us, we’re not quite sure what we should sell. To succeed in online retail, you need a product that is trending upwards in a growing niche.
Different types of products
Some of the different types of products include the following:
- Convenience products: Frequent purchase products, little effort on buying
- Shopping products: Less frequently purchased in between purchases, little more effort and planning, shop around
- Specialty products: Strong brand preference and loyalty, will buy no matter what the price
The various types of niches include the following:
- Hobby niches
- Lifestyle niches
- Problem niches
- Weird/embarrassing niches
Existing products
Come up with detailed specifications for each product or service you intend to sell. If it’s a hiking shirt we’re selling, we would want to have:
- Detailed sketches of the shirt
- Fabric weight, materials, type
- Key features (e.g., pre-shrunk, water-proof, SPF 40)
Future product pipeline
What are other products that you have in the pipeline? Perhaps once you’ve successfully sold hiking shirts, you’re able to leverage your manufacturing relationships to provide hiking socks and shorts. Include that information in this section.
The products and services section will cover the various selling categories of items.
These product offerings will include the following:
- Tripwire
- Core product
- Cross-sell
- Upsell
- Additional
Each product group will have its own purpose in your sales catalog. For example, tripwire is the product that brings customers to your ecommerce store or online marketplaces while the core product is your main seller.
Knowing what products you’ll include within each section allows you to have a firm grasp on what your main product will be and how the other types of products will work alongside your main product.
This section will also cover the search volume and Amazon pricing range.
You’ll need to calculate your true costs. You have to make sure you don’t overestimate your margins.
To tabulate your total true costs, you need to write down the costs in the following areas:
- Target price
- Supplier cost of the product
- Total cost per unit
- Net profit per unit
- Profit margin per unit
Once you complete the pricing portion, you’ll have everything on one sheet and readily accessible whenever you need it.
Marketing Plan and Operations

So, now you’ve concluded that you have a great business idea, and it’s in a growing market. That’s fantastic – but how are you going to drive traffic to your ecommerce website and get customers to buy it? And how much can you afford to spend on your product?
Marketing is everything. It’s important that your marketing efforts match your business model.
If you have a website and no marketing, your site won’t have any visitors. With no visitors, you will make no sales. Then how do you grow and sell your ecommerce business(if that’s your long-term goal)? Even with the best possible products, nobody will buy them if they aren’t directed to them in some way.
In order to come up with a marketing strategy, you need to first know your customer inside out. You should be able to answer such questions as:
- How old is your customer?
- Where does your customer live?
- What is the population of your customer base?
- What is their education level?
- What is their income level?
- What are your customer’s pain points?
With so many channels to reach your customer, which one is best for you?
Once we know pretty much everything there is to know about our target customer, we can shift focus to our marketing strategy. You want to choose marketing strategies that equal positive conversion rates. What channels should you use to grab the attention of your customer demographic? Some of the key marketing channels include:
Paid Marketing
- Pay-per-click – this online marketing typically involves using Google Shopping campaigns and managing a product data feed.
- Affiliate sales networks – Allowing other blogs and websites to sell your product for a cut of the revenue. List the different affiliate sale networks that you plan to promote through.
- Facebook ads ⎯ Ads posted on Facebook to draw in buyers through social media means.
- Influencer marketing ⎯ Hiring industry influencers to get the word out about your product through their social media platforms and contacts.
Organic Marketing
- Social media (Facebook, Instagram, Pinterest, etc.): What is your strategy for social media, and where will you dedicate your attention?
- Search Engine Optimization: Create and promote awesome content so people find your product organically through search.
- Content marketing: Figure out how you’ll use content marketing in your business. Consider various article topics that will persuade your target audience to buy your products.
- Blogger networks: could be organic or paid through affiliate sale programs.
- Key bloggers: Develop a list of the key bloggers in your product category. For Atlas Hiking Co., this might be an influencer that blogs about the best hiking trails in America.
Finding the optimal mix of these advertising tools depends 100% on your customer segment as well as your product type. For example, a SaaS product targeting millennials will require an entirely different marketing strategy than an e-commerce physical product targeting baby boomers. Perhaps that should be a post on its own for another day!
How much should you spend to acquire a customer?
In order to understand this, we need first to discuss a concept known as customer lifetime value or LTV. In essence, this is a formula that helps you better understand how much an average customer will spend over time.
Here’s a good read on how to calculate LTV.
It’s important to remember that for new businesses, you don’t have a lot of data on customer purchase habits so it’s a good idea to be more conservative with your assumptions in calculating LTV.
Let’s say, for Atlas Hiking Co., I determine that the average LTV per customer is $300. This means that over time, the average customer will spend $300. Let’s say, on average, if I receive $300 in revenue, $100 of that will translate to gross profit before I factor in my marketing costs (basically, I’m just subtracting the cost of making the shirts).
Knowing that my gross profit is $100 per shirt is a critical piece of information because it tells me that I can spend up to $100 in marketing to acquire a customer and still be profitable!
Some of the marketing options include social media marketing and content marketing.
Think about your business model and then line up your marketing budget. Your marketing budget may include the following items:
- Sales/branded content
- SEO/blog content
- Facebook/Instagram ads
- Influencer marketing
- Profit margin per unit
- Marketing tools
- Niche advertising
Choosing The Right Technology
With so much technology and SaaS products out there, it’s important to understand the various moving parts and diagram how they all integrate with one another.
Some of the different elements include:
- Shopping Cart Platforms – e.g., Shopify, BigCommerce, WooCommerce, or any open-source platform
- Hosting – Nexcess, BigScoots, Kinsta, WPX
- Payment Processor – e.g., Stripe, Paypal
- Fulfillment Center – e.g., Amazon, ShipBob
- Apps – e.g., Zipify, BuildWooFunnels, Gelato
- Accounting & Taxes – e.g., Quicken, Xero
- Marketing Automation – e.g., Klaviyo, Mailchimp
- Marketing Tools – e.g. Buzzstream, Ahrefs
- Customer Loyalty Programs – e.g., Antavo, Smile
Come up with a detailed list of the different products and services you need to run your business as well as the monthly and per-transaction cost of each of them. This will be important in understanding the impact of these services on your margins.
Matching your business model to your technology is essential, too. Certain website platforms are better suited for specific sales models.
Email marketing is another type of technology that should be carefully considered and matched up correctly with your business model.
Keep in mind that it takes, on average, 6-7 interactions with a brand before someone makes a purchase, so you need to keep using technology to get them back to your website.
As you explore the technology options and find out ways to draw potential customers in and keep them happy while they’re there, here are some key points to keep in mind:
- What you say about yourself and your products with your website content
- How you respond to questions on live chat and email support
- How to make use of chatbots
- How you connect on social media
- The information you send through email marketing
- What bloggers and influencers say about your brand
- How existing customers review your company
- How you advertise
- How you establish loyalty beyond sales
After you figure out your technology methods, you have to come up with a technology budget.
The business plan must also include the operations side of things. Determine who will be your manufacturer, secondary manufacturer, and shipping and fulfillment provider.
When looking at supply chain costs and options, ShipBob is an ecommerce fulfillment provider you can consider.
Financial Plan

When figuring out your financial plan, evaluating and pinpointing your startup costs is essential.
The focus of the financial plan is how long it will take for you to make your money back. You also need to figure out if you need a business loan.
Traffic and conversion rates will help you determine how long it will be until you start making money back.
You’ll also want to use an income statement to detail financial information.
This section is used for financial projections, such as forecasting sales, expenses, and net income of the business. Ideally, you’ll want to create a monthly Excel balance sheet showing the following:
- Projected revenue: First, come up with your projected number of units sold and then come up with your projected revenue (Projected Revenue = # of Units Sold * Average Sales Price).
- Fixed expenses: these are expenses that are fixed no matter how much you sell. Typically, these relate to monthly SaaS subscriptions, employee salaries, or rent.
- Variable expenses – these expenses change in direct proportion to how much you sell. Common examples include the cost of goods sold and credit card payment processing fees.
This helps business owners better understand what they need to achieve to hit their profit goals. In reality, projections are usually always off the mark, but it’s good to give yourself some measurable goals to strive for.
This section should aim to answer the following questions about your product offering:
- How much product do you need to sell per year to meet your income goals for the business?
- What are the margins on your product? If you sell one hiking shirt for $50, how much do you make after paying your supplier, employees, and marketing costs?
- What is the lifetime value of a customer?
- How much can you spend to acquire customers? If you conservatively project that the average customer will spend $300 over time on your shirts, then you can afford to spend an amount less than $300 to acquire that customer using the paid marketing channels described previously.
- Do you have any big capital expenditures early on that would require you to need to bring in investors?
- Can you improve gross margins by making bigger orders from your suppliers?
There are various acquisition channels that will help your traffic to convert including:
- Direct
- Organic
- Adwords
- Referral
- Social
Your revenue plan will contain a 12-month revenue forecast plan to help you map out each month of earnings.
There are different business earning models you can go through to determine how much you can make with your business.
You want to calculate how much traffic costs. This all depends on the methods you use to gain traffic to your site.
As you determine what your profit might be with your ecommerce business or ecommerce businesses, there are certain math formulas to use:
- The profit equation
- Break-even analysis
- Units needed to achieve the profit target
You should also consider how you will use fintech companies in your ecommerce business.
FAQs
Wrapping Up Your Business Plan
Careful planning is crucial to get your e-commerce business from the planning phase to the launch phase and to ensure its successful future.
Going through the exercise of writing a business plan will cement your own understanding of your business and your market. It will also position you to take advantage of lucrative opportunities while mitigating harmful threats to your business down the line.
Your turn! Have you written a business plan for your online store? Do you have anything to add? Tell us about it in the comments below!









