An SSL certificate is also known as a secure sockets layer certificate or SSL/TLS. TLS stands for transport layer security.
It is a digital certificate that authenticates a website and allows for an encrypted connection. It’s what makes the difference between a website at HTTP://domain.com and HTTPS://domain.com. If you want or need an HTTPS web address, you have to have an SSL certificate.
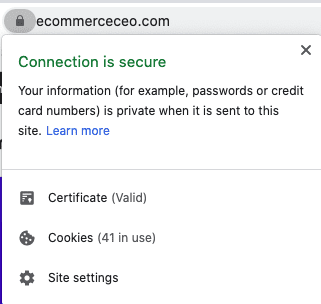
The “s” stands for “secure.” Many browsers will display a green padlock in the address bar to indicate that you have a secure connection. Some web browsers just display a padlock.

If you ever want to know more about a website’s security, click that padlock. It will display details about the certificate, including its expiration date.
It’s necessary for any websites that will send or receive sensitive information – such as ecommerce websites. And, Google recently made it a ranking factor. Even if you operate a blog that exchanges no personal data, an SSL certificate will boost rankings. It will also build credibility and increase your trust with your audience.
SSL Certificates Explained
An SSL certificate digitally connects a cryptographic key to a business’s details. You’ll know the website your visiting uses SSL when you see the little padlock icon in your web browser.
The SSL certificate binds:
- The domain name, hostname, or server name
- Organizational identity – company name and location.
An SSL certificate contains a great deal of information, which helps to keep user data secure, including:
- The domain name the certificate was issued for
- Associated subdomains
- The person, organization, or device it was issued to
- The issuing certificate authority
- The issuing certificate authority’s signature
- Certificate issue date
- Certificate expiration date
- The public key (a private key is also issued but remains secret)
Once it’s installed on your server, the connection between your web server and your visitors’ browser is secure.
How Does an SSL Certificate Work?
SSL TLS works thanks to public-key cryptography.
With this type of cryptography, there are two keys. Each key is a long string of randomly generated numbers.
One key is a public key. Your server knows this key. That key is available in the public domain. The key can encrypt any message.
The other key is a private key. Your domain is the only one that has this private key. It is required to unlock any messages encrypted with your public key.

For instance:
If Cindy wants to send a message to Adam, she can lock it with Adam’s public key. But, the only way to decrypt the message is to unlock it with Adam’s private key.
Adam is the only one who has this private key, so he is the only one who can unlock Cindy’s message.
If a hacker were to intercept the message before Adam unlocks it, they would see a random code. This code is so strong that the hacker couldn’t even use a computer to break it.
Let’s look at it in terms of a website and a server, sending and receiving information. The website and server are Cindy and Adam.
What is the Purpose of SSL Certificate?
An SSL certificate creates a secure connection between the web server and other computers. The idea is that the information transmitted between servers is encrypted. This makes it harder for hackers to access the information.
It also helps to verify ownership of the website and prevent hackers from creating fake versions of a website.
What kind of information does an SSL certificate help secure?
- Your login credentials, including usernames and passwords
- Bank account information and credit card numbers
- Personally identifiable information – your name, date of birth, address, telephone number
- Medical records
- Legal documents
- Proprietary information
Ultimately, it makes the web a safer place to share data.
Types of SSL Certificates
There are several types of SSL certificates to choose from. What you need depends on the nature of your website. If you are doing a lot involving personal user data, you may want a stronger certificate.
All certificates do a good job securing user data and encrypting web traffic. They come with trust seals to help visitors. The extra validation builds trust and credibility.
Domain Validated Certificate
Also known as a DV certificate, this is a basic SSL certificate. The CA checks to make sure the applicant has the right to use a specific domain name. This is known as domain validation. No company information is vetted. No additional information is displayed.
Domain validation requires information to be sent to the website’s registered email address. This verifies access to the domain.
Since no company information is vetted, all you’re doing is verifying server identity. This ensures no fake sites are trying to steal information. As such, the certificates are issued relatively quickly.
DV certificates ensure that your information is encrypted. They do not guarantee that the organization is who they say they are. You don’t know who is receiving the information shared with the site.
Organization Validated Certificate
Also known as OV SSL, this is one step above the DV certificate. With OV certificates, the CA also vets some of the organization’s information. The additional vetted information is displayed whenever someone clicks the padlock.
Your website visitors can see information about the organization behind the website.
Since some information needs to be verified, these certificates aren’t issued right away.
EV SSL Certificate
The extended validation option is the one recommended for ecommerce businesses. It takes the longest to issue because a lot of business information is verified, including:
- Your organization’s legal name – and that your organization is in good standing
- Your exact organization trade name, including any doing business as (DBA), if applicable.
- Your business’s respective owners and who controls the domain or domains listed on the certificate.
- Your organization’s main telephone number
As such, you’ll need to provide corporate documents like your articles of incorporation, EIN, and Dun and Bradstreet (D&B) listing (even if you don’t have business credit) to make it easier to verify everything. On your application, list your legal business name, not your DBA. Use the address where you conduct business instead of a PO Box.
Single Domain SSL Certificate
This kind of SSL will protect a single domain only. It will not cover any subdomains attached to the domain. You cannot use it to secure multiple domains.
Wildcard SSL Certificates
SSL/TLS wildcard certificates are a single certificate that uses a wildcard (*) symbol in the domain name field. This wildcard means that you can use the certificate to secure multiple subdomains that relate to the same base domain.
For instance, you can use a wildcard certificate for *.domainname.com to secure:
- www.domainname.com
- mail.domainname.com
- store.domainname.com
- Any other subdomains on domainname.com.
You cannot get an EV wildcard SSL certificate for security reasons, so if you want to secure multiple subdomains with EV SSL, you need a multi-domain SSL.
Multi-Domain SSL Certificates
If you need an SSL certificate for more than one domain, a multi-domain SSL certificate. It secures multiple domain names under a single IP address.
The certificate is issued with additional alternative domain names listed on it. This ensures you can install one certificate to protect all the domains on the approved list.
Free SSL Certificate
You can get a free one from Let’s Encrypt. It’s a non-profit organization that issues certificates. They want to create secure connections across the entire internet.
There are some key differences, though.
The free option still provides SSL encryption, but it has to be renewed every 90 days. They do not offer support due to limited resources. It can be challenging to know how to install and renew them.
A major issue is that while they provide website security, many browsers won’t issue the padlock. They may still alert users to an unsecured connection.
How Do I Get an SSL Certificate?
You can get an SSL certificate in two ways. You can buy one directly from a certificate authority. Or, you can buy through your web hosting provider. All SSL certificates must come from a certificate authority.
So, even if you purchase it from your web host, they act as a middle-man. They do this to make it easier to install the certificate on your domain.
A certificate authority is a trusted organization that manages and issues security certificates and public keys. Popular certificate authorities include:
- GlobalSign
- Verisign
- Sectigo
- Let’s Encrypt
- Comodo Cybersecurity
- DigiCert
First, you have to determine the right SSL certificate for your needs. If you’re hosting content across separate domains and subdomains, you may need different SSL certificates.
For most people, a standard SSL certificate covers your bases. If you’re a company in a regulated industry – like insurance or finance – you’ll need more protection. Your industry has set SSL certificate requirements that you’ll need to follow.
Once you know the kind of certificate you need, you’ll have to pay for the certificate. You’ll pay the company you’re buying the certificate from. Most of the time, you’ll pay annually.
You’ll have to follow instructions from the vendor to generate the certificate. If you use a shared hosting plan, your host will require you to purchase a dedicated IP address. This has to be done before the server’s SSL certificate can be installed.
When it comes to ecommerce, you want extended validation, the highest level of security. Since you’ll be collecting personal and financial data, it’s crucial. It protects your business should there ever be a data breach and helps build trust with your consumers.
You’ll need to supply documentation to verify your business. The purpose of the certificate is to validate that you are who you say you are. The more documentation you can provide to make it easier, the better.
Once the information is validated, your certificate will be issued. The certificate then has to be installed on your server. If you’re not tech-savvy enough to do this yourself, someone on your web host’s tech support team can handle it for you.
A Note About Ecommerce Platforms
If you use an ecommerce platform like Shopify or BigCommerce, SSL/TLS is included.
You’ll only need to invest in SSL if you plan on hosting your ecommerce store yourself.









